Git使用与理解
参考:git pro,git-scm.com/blog, Think Like (a) Git
1. 分布式
集中式版本管理(如svn):
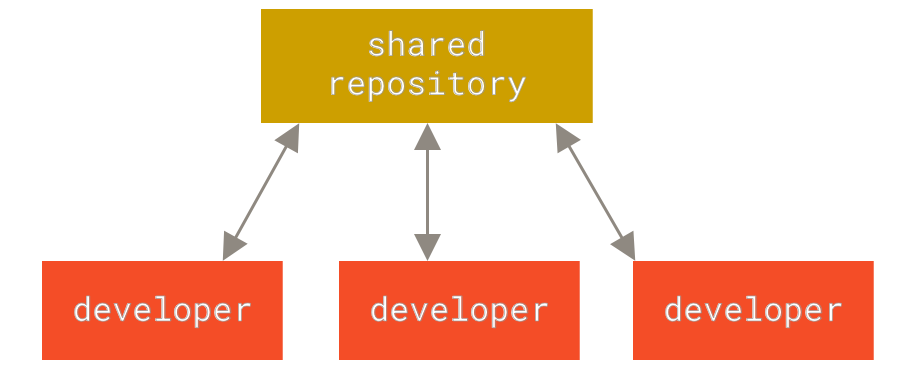
分布式版本管理:
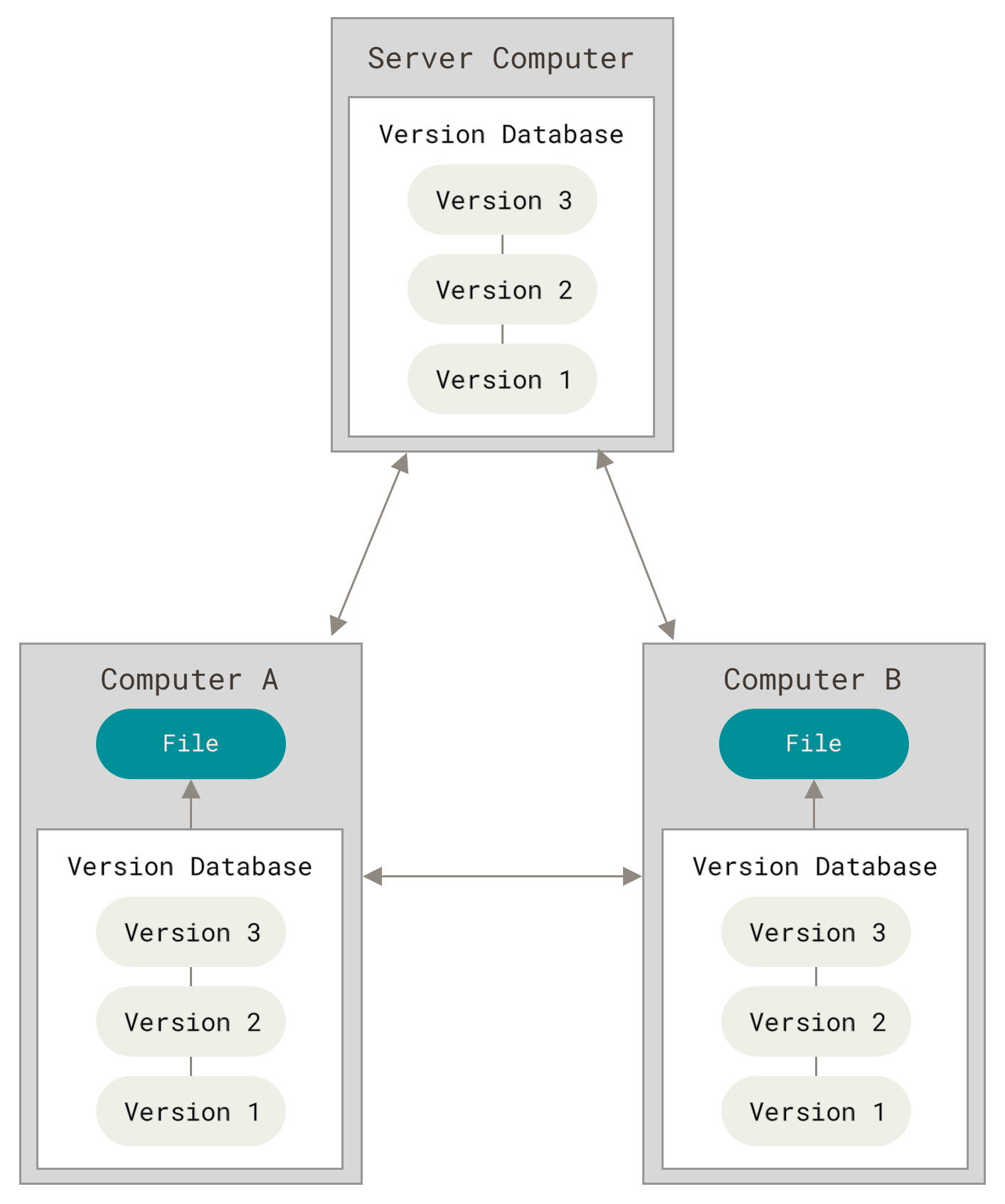
演示iSource和两个个linux主机间同步
git clone xyc@100.120.252.146:/local/workspace/gittest
集中式服务器宕机和磁盘损坏都是很严重的问题,分布式每台机器都拥有完整的仓库信息,所有操作基本都在本地进行。
2. 基于快照
增量式版本控记录(svn):
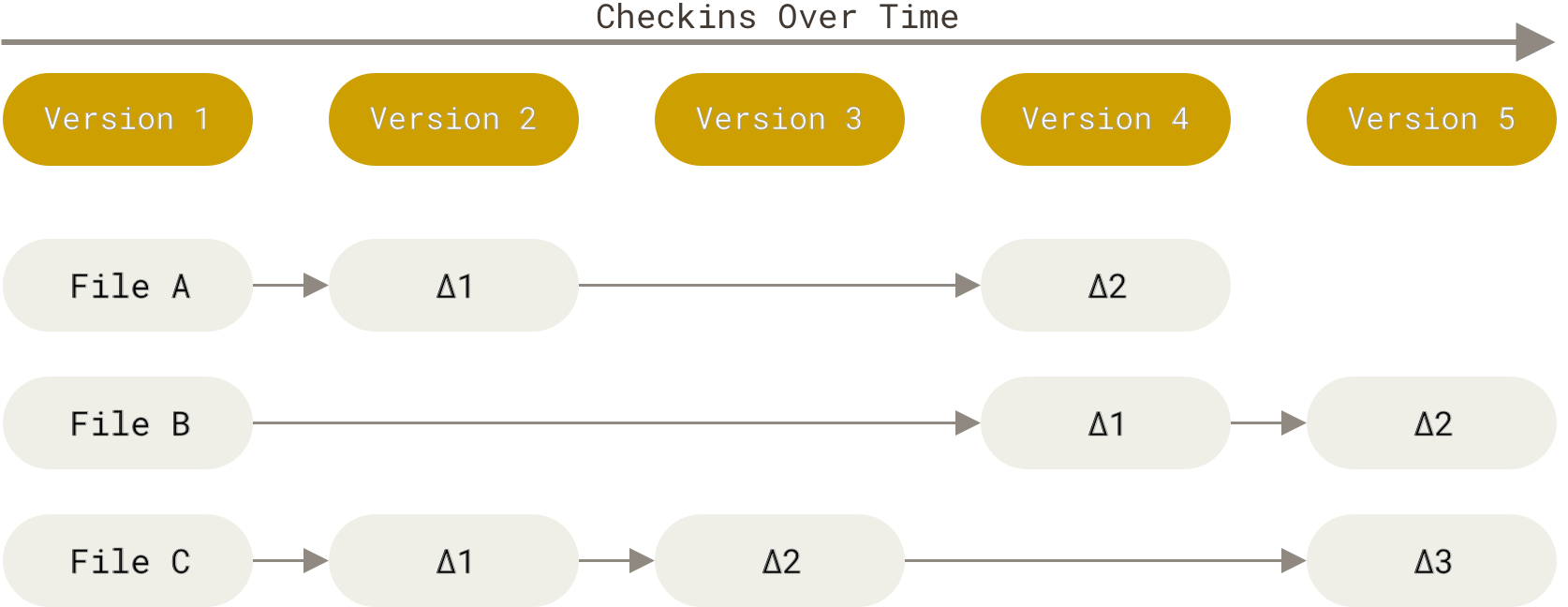
快照式版本记录:
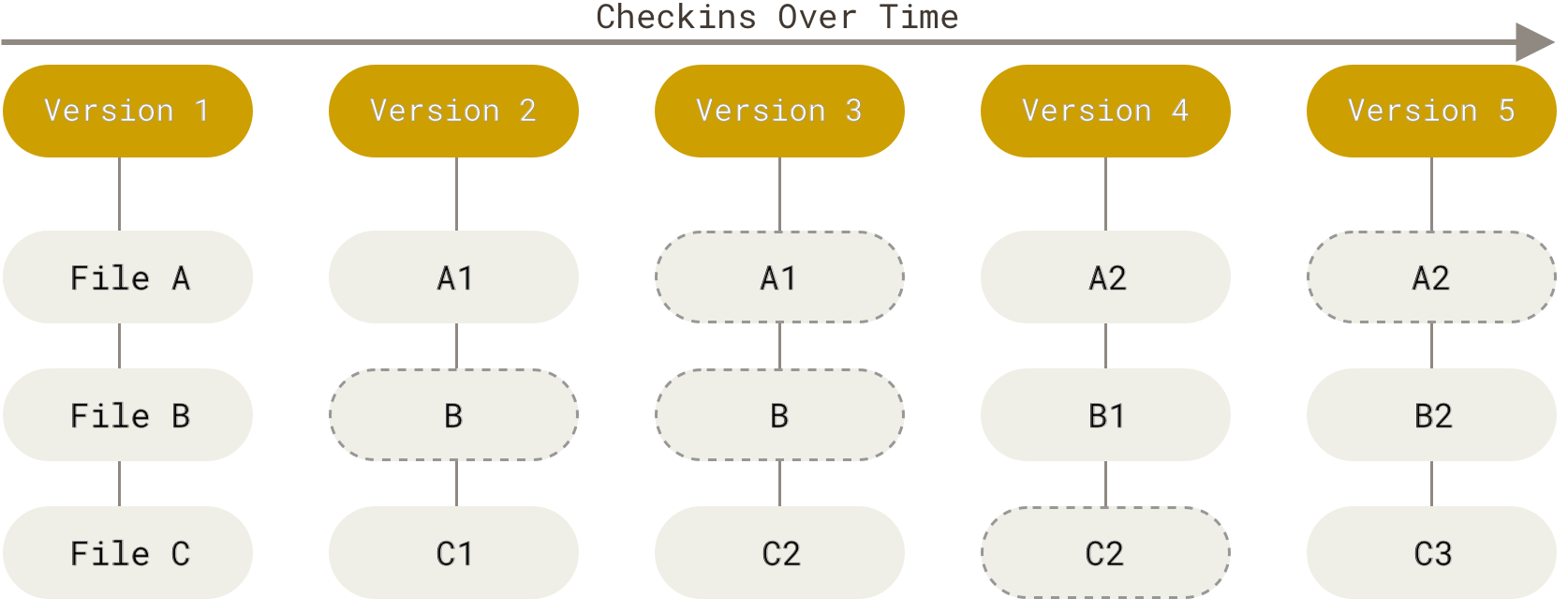
基于快照让git像一个文件系统,很多地方采用了引用,相对于增量式,更加简单,也因此功能更强大,分支操作也更高效。
基于快照存在的问题:
对于大文件的修改,即使修改很小,也会同时记录两份文件,浪费空间。

为此对于大文件需要采用另外一种机制,Git LFS,参考:Learn Version Control with Git和Git LFS-Tutorials。

3. 三种状态、三个区域、三棵树
三种状态:
- committed:已经提交到数据库的修改
- modified:没有记录的修改
- staged:已经记录将要提交到数据库的修改,相当于缓存
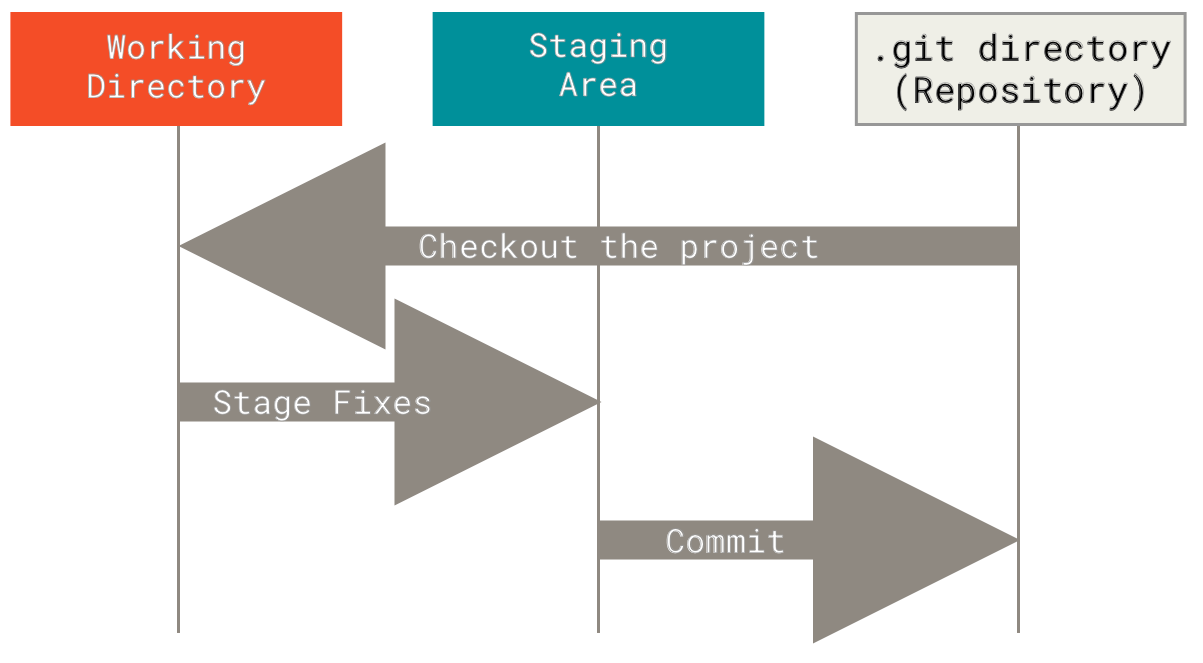
演示流程
三棵树:
- HEAD:last commit snapshot, next parent
- Index:proposed next commit snapshot
- Working Dir:sandbox

4. 文件的生命周期
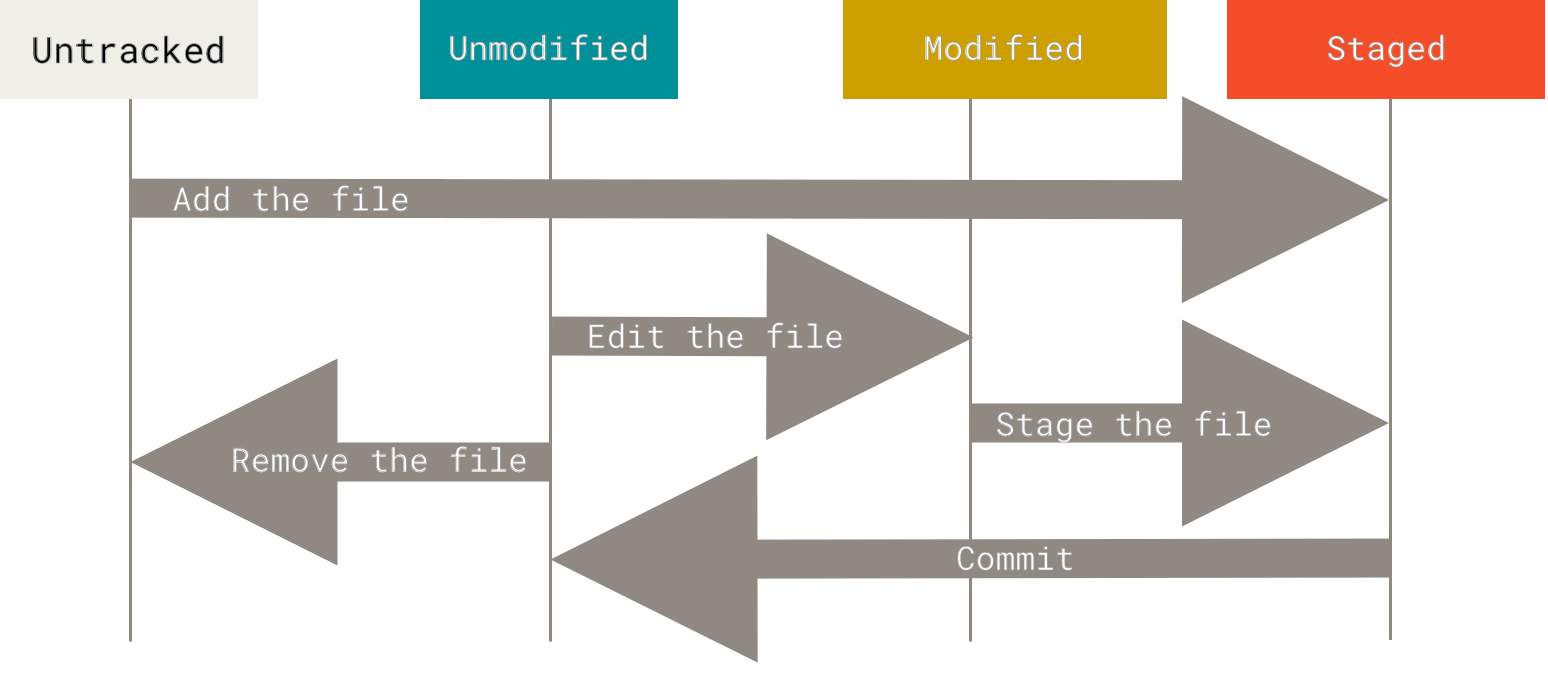
5. 基本操作:clone、record、view、undo、remote
clone主要有三种协议:http(s)://path/to/repo.git,git://path/to/repo.git, user@server:path/to/repo.git
http(s)://path/to/repo.git零配置,手动输入用户名密码git://path/to/repo.git配置sshkey,基于sshuser@server:path/to/repo.git基于ssh,主机间
record常用操作:
- git add
Add file contents to the index - git status
Show the working tree status$ git status -s ?? file1.txt // aren't tracked A file2.txt // new file added to staging area AM file3.txt // new file in staged area modified M file4.txt // file modified in workspace MM file5.txt // file modified in staging area and workspace D file6.txt // delete with git rm in both area R file1.txt -> file.txt // rename file in both area左侧状态相对于HEAD,右侧状态相对于INDEX
- git commit
Record changes to the repository - git rm
Remove files from the working tree and from the indexgit rm --cached file1.txt // delete file just from staging area - git mv
Remove files from the working tree and from the index
view用来查看版本历史:
- git log
git log --graph
undo:
-
git commit –amend
撤销一次commit,在过早提交时有效 -
git reset HEAD <file>...unstaging a staged file -
git checkout -- <file>Unmodifying a Modified File
remote:
-
git remote
查看当前的远程分支 -
git fetch [remote-name]
同步远程分支 -
git push [remote-name]
推送本地修改 -
git pull [remote-name]
等同于fetch和merge
5. 分支、合并
一次commit的数据模型:
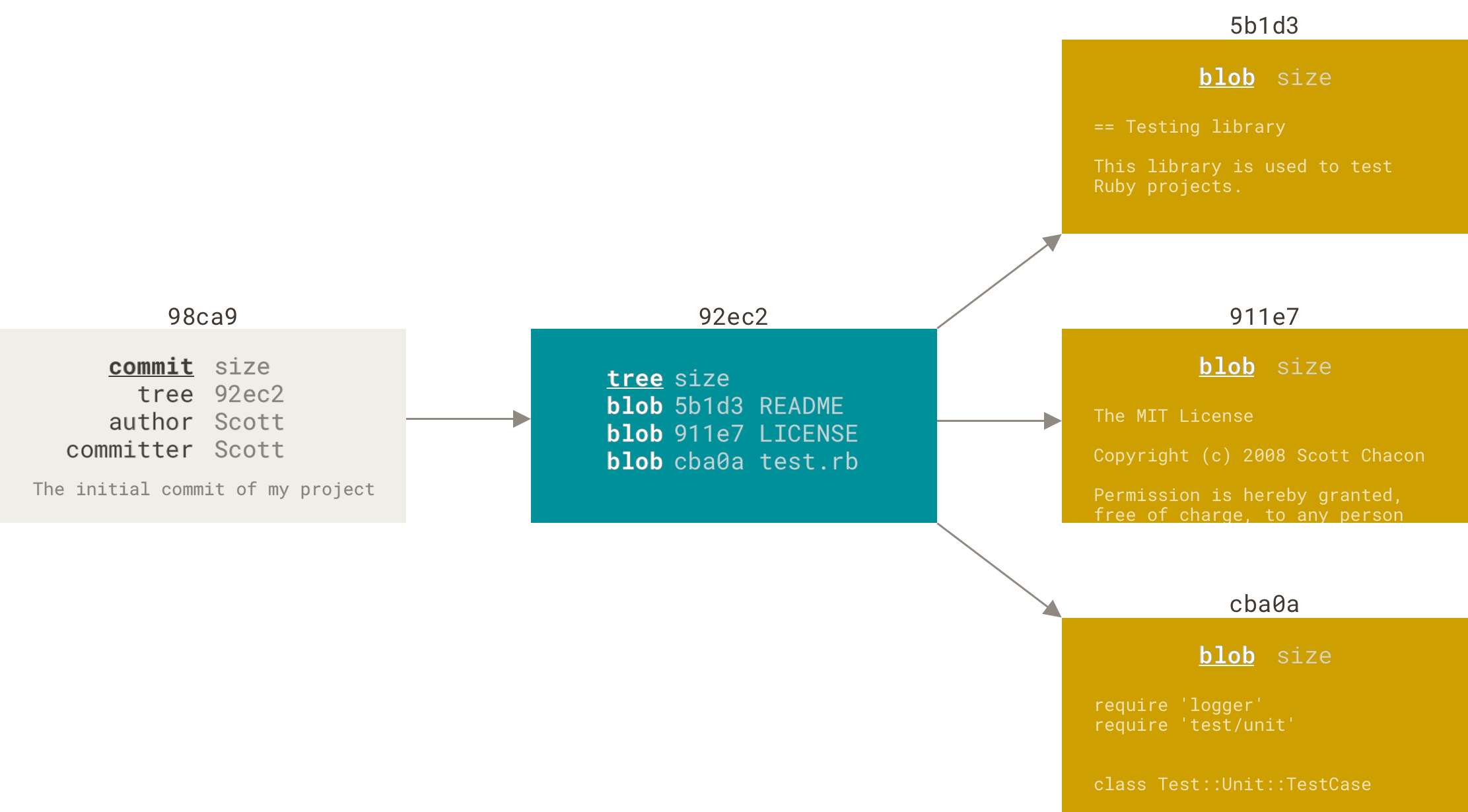
commit之间的关系:
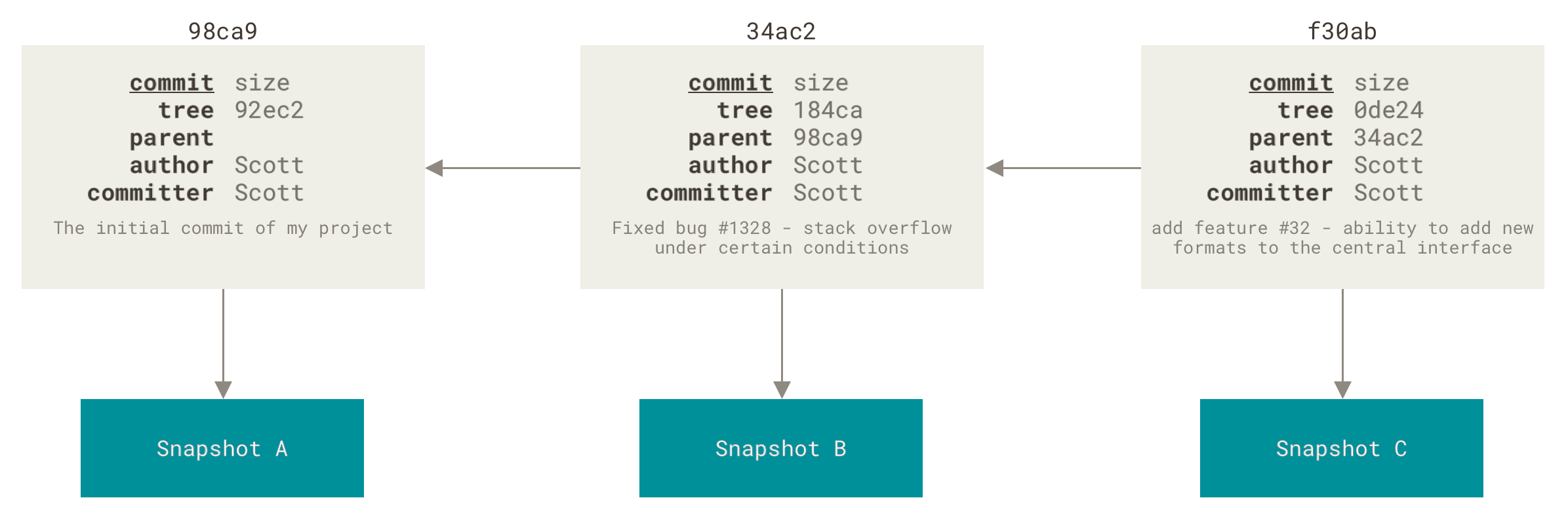
新建分支:
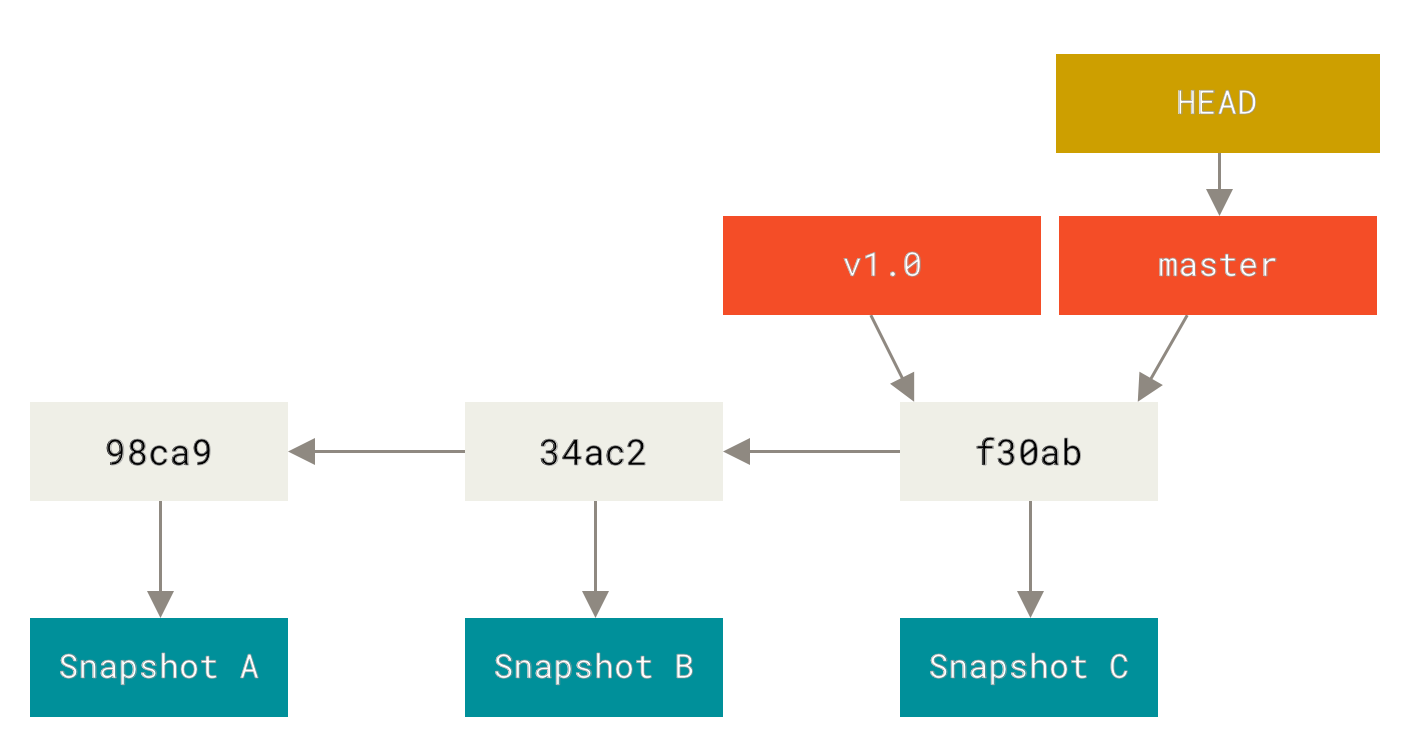
-
git branch -b xxx
新建分支 -
git merge xxx
合并分支 -
git checkout xxx
切换分支
正因为git的分支模型如此,分支操作才不会像svn是通过复制文件夹来实现。
6. reset
图片挂了,后续补充。
基本操作:





合并一些提交:



reset branch:

FAQ
合并git记录
主要用到git的squash选项,参考:
- Squash my last X commits together using Git
- How can I merge two commits into one?
- Rebasing a Git merge commit
当commit中存在merge的commit时,可能上述方法就不能奏效,这是可以基于origin/master创建一个分支,然后从包含commit记录的分支合并过来,参考:Merge all changes from another branch as a single commit
git merge --squash <feature branch>
删除local和remote分支
参考stackoverflow, 删除remote
git push origin --delete <your_branch>
删除local
git branch -D <branch_name>
What’s the difference between HEAD^ and HEAD~ in Git?
There is no tracking information for the current branch.
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/<branch> master
warning: LF will be replaced by CRLF in bootstrap/css/bootstrap-theme.css
Unix采用LF形式,可以通过input选项将windows checkout保持在crlf,而unix还是lf,参考stackoverflow
git config --global core.autocrlf input
server certificate verification failed. CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt CRLfile: none
git config --global http.sslverify false
Pointer file error: Unable to parse pointer at: “xxx”
可以看看https://github.com/git-lfs/git-lfs/issues/1828 以及https://github.com/git-lfs/git-lfs/issues/1113 重点是理解lfs
其他
-
找回没有引用的commit,参考reflog
- merge和rebase的区别:
- merge如实记录版本过程
- rebase简单化版本过程
- 理解diff输出,参考How to read the output from git diff?